Anti-Human ApoE (Pan) - Purified No Carrier Protein
Catalogue Number: A458-LET
| Manufacturer: | Leinco Technologies, Inc |
| Type: | Monoclonal Primary Antibody - Unconjugated |
| Shipping Condition: | Blue Ice |
| Unit(s): | 1 mg, 100 ug |
| Host name: | |
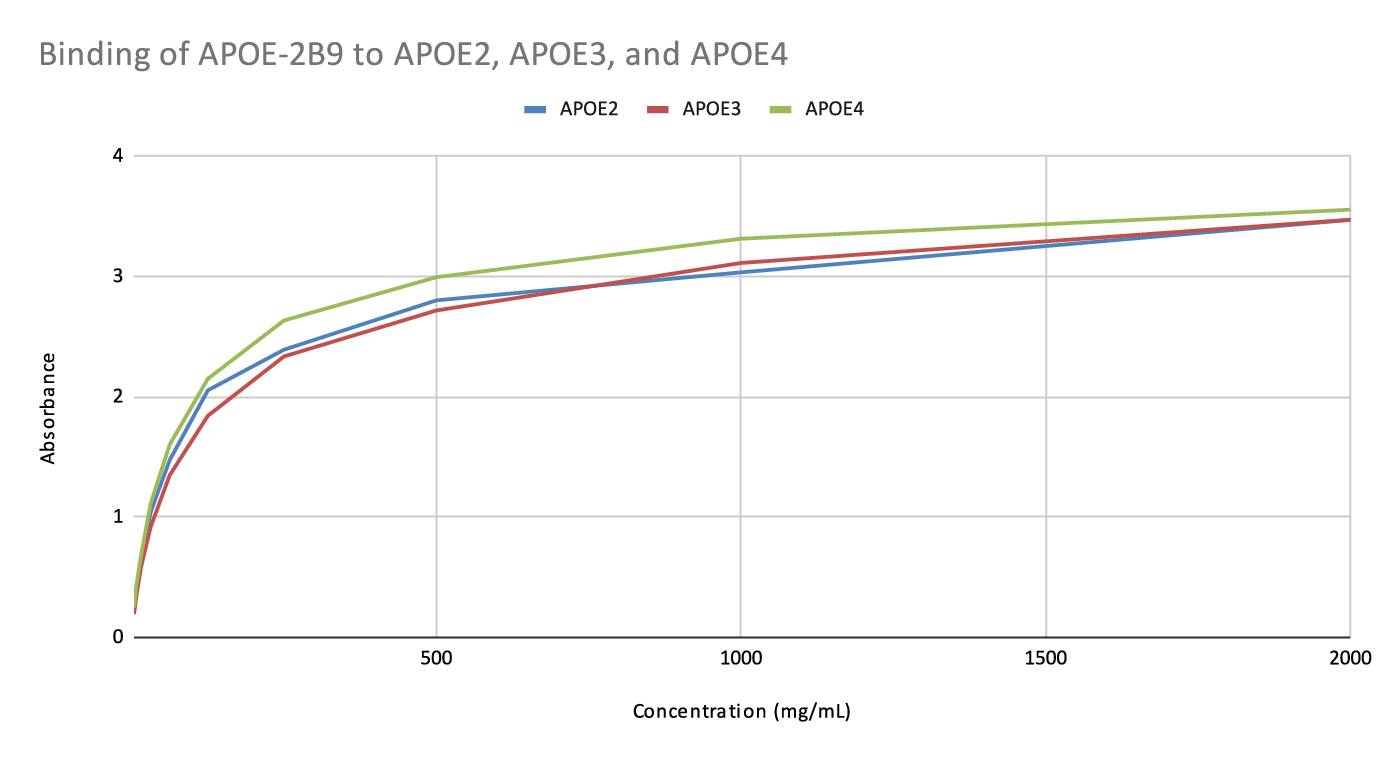
| Clone: | ApoE-2B9 |
| Isotype: | |
| Immunogen: | |
| Application: | ELISA, WB |
Description
Description: ApoE is a 299-amino acid multifunctional protein primarily synthesized in the liver, but also produced by other tissues including the brain. It is a major component of several classes of lipoproteins, including chylomicron remnants, very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDL), and some high-density lipoproteins (HDL)1. It plays a crucial role in lipid metabolism and has significant implications for various diseases, particularly neurodegenerative disorders1. The primary function of ApoE is to mediate the binding of lipoproteins to specific cell-surface receptors, particularly the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR). This interaction is essential for the normal processing and catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins1. In the central nervous system, ApoE is mainly produced by astrocytes and plays a crucial role in transporting cholesterol to neurons via ApoE receptors1. There are three major isoforms of ApoE in humans: ApoE2, ApoE3, and ApoE4. These isoforms differ by only one or two amino acids at positions 112 and 158, but these small differences have significant impacts on their structure and function1. The ApoE genotype has been strongly associated with various diseases: 1. Alzheimer's Disease: The ApoE4 isoform is the strongest genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Individuals carrying one copy of the ApoE4 allele have a 3-4 fold increased risk, while those with two copies have a 12-15 fold increased risk1. 2. Cardiovascular Disease: ApoE plays a role in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease risk. The ApoE4 isoform is associated with higher levels of LDL cholesterol and increased risk of coronary heart disease1. 3. Lipid Disorders: The ApoE2 isoform is associated with type III hyperlipoproteinemia, a rare lipid disorder characterized by elevated levels of cholesterol and triglycerides. 4. Other Neurological Conditions: ApoE has been implicated in other neurological disorders, including Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, and traumatic brain injury1. The mechanisms by which ApoE influences disease risk are complex and not fully understood. In Alzheimer's disease, for example, ApoE4 is thought to affect amyloid-β aggregation and clearance, tau phosphorylation, neuroinflammation, and synaptic plasticity1.
Additional Text
Purification
Purified
Antibody Clonality
Monoclonal
Concentration
1 mg/ml
Storage Note
Antibodies may be stored sterile as received at 2-8°C for up to one year. For longer term storage, aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at ≥ -80°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles.